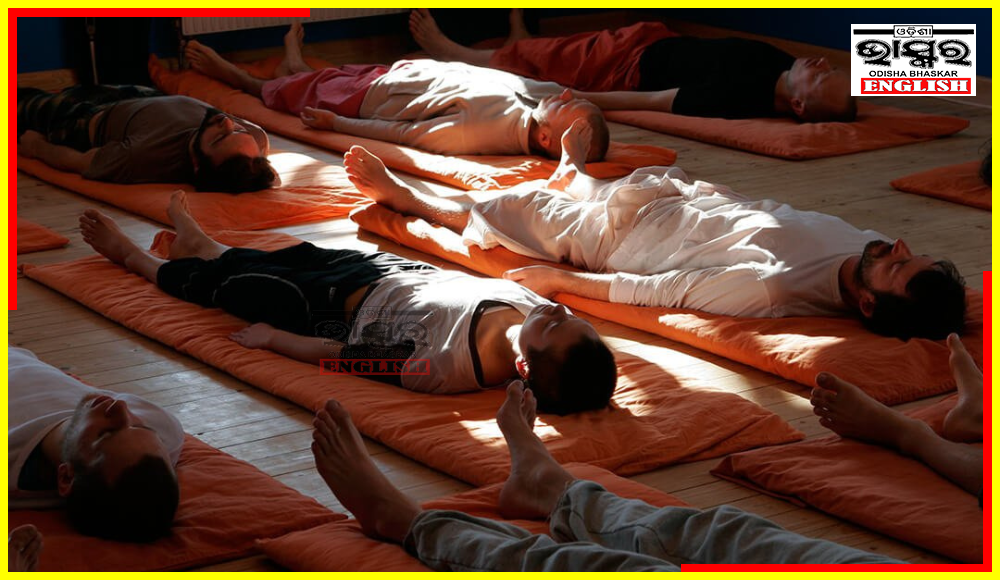
New Delhi: Researchers from IIT Delhi, AIIMS Delhi, and Mahajan Imaging Delhi have proved the immense benefits of Yoga Nidra, the conscious yogic sleep practice.
These researchers explored the effects of Yoga Nidra by scanning brains with functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) technology. Their finding, exploring the neural mechanisms underlying Yoga Nidra was published in the international journal Scientific Reports.
According to a release by the Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, the study, titled “Functional connectivity changes in meditators and novices during ‘Yoga Nidra’ practice,” included two groups: 30 meditators (householders with an average of 3000 hours of experience in meditation and/or yogic practices) and 31 matched novice controls. The study found that the Default Mode Network behaves differently (less connected) in experienced meditators compared to novices. This difference in brain communication patterns helps us understand how ‘Yoga Nidra’ modulates our brain functions, promoting a state of deep relaxation while staying aware.
The study found a strong link between the amount of meditation and yoga practice participants had and the reduction in DMN connectivity during ‘Yoga Nidra’. In other words, the more hours participants spent practicing meditation and yoga, the more noticeable the changes in their brain activity during ‘Yoga Nidra’.
These results could potentially indicate that experienced meditators have reduced mind-wandering as compared to novices, leading to changes in the DMN connectivity.



Comments are closed.