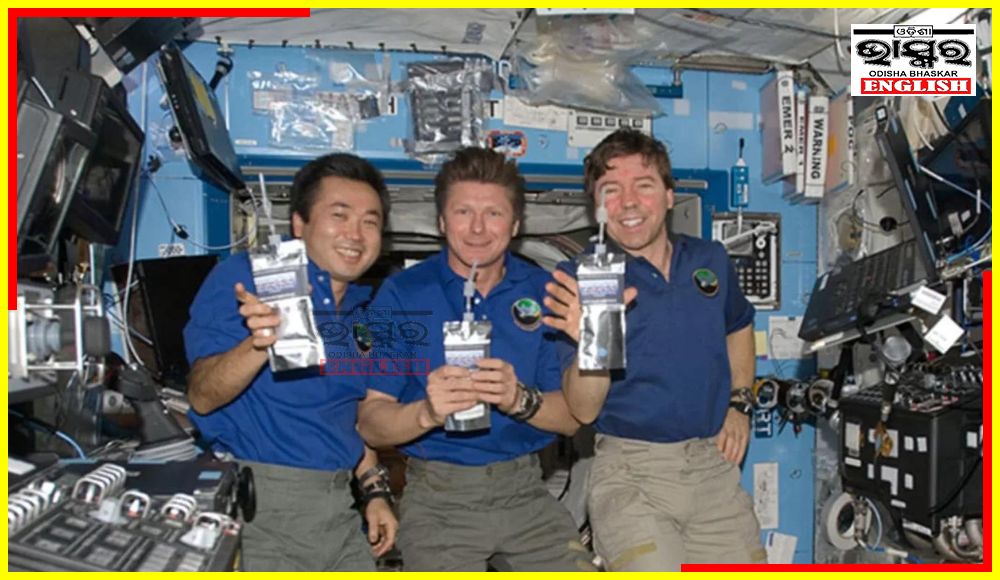
In a major breakthrough for future space missions, astronauts aboard the International Space Station have attained a 98% water restoration using a system that includes recycling of astronauts’ urine and sweat.
Through this process urine and sweat of astronauts are recycled into completely drinkable water. This achievement will help in longer space travels. Any space mission including the astronauts aboard ISS needs around a gallon of water every day for drinking, food preparation, and hygiene uses.
This ultimate water recovery was possible due to the sub-systems that are part of the Environment Control and Life Support Systems (ECLSS) that recycles consumables such as food, air, and water for further use in space.
Another subsystem, the Urine Processor Assembly (UPA), recovers water from urine using vacuum distillation. A Brine Processor Assembly (BPA) was added to the UPA to extract this remaining wastewater from the residue brine produced by the UPA. The BPA increased the amount of clean water extracted from urine from 94% to 98%, the highest so far.
It is claimed that this recycled water is cleaner than what we drink here on Earth.


Comments are closed.